W. Yang, et al., J. Appl. Phys. 115, 203105 (2014).
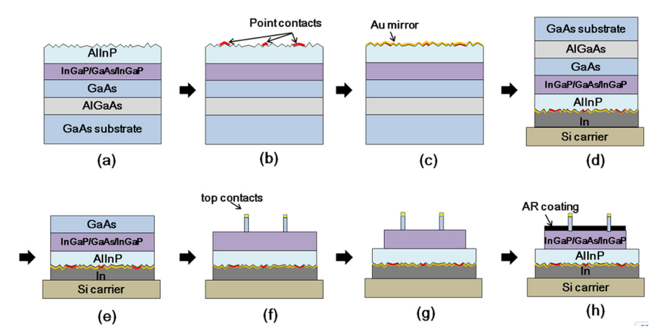
This paper reports the proposal, design, and demonstration of ultra-thin GaAs single-junction solar cells integrated with a reflective back scattering layer to optimize light management and minimize non-radiative recombination. The structure of the demonstrated solar cells consists of an In0.49Ga0.51P/GaAs/In0.49Ga0.51P double-heterostructure PN junction with an ultra-thin 300 nm thick GaAs absorber, combined with a 5 µm thick Al0.52In0.48P layer with a textured as-grown surface coated with Au used as a reflective back scattering layer. Solar cells with a top metal contact coverage of 9.7%, and a MgF2/ZnS anti-reflective coating demonstrated open-circuit voltages (Voc) up to 1.00 V, short-circuit current densities (Jsc) up to 24.5 mA/cm2, and power conversion efficiencies up to 19.1%.
S. Liu, et al., IEEE J. of Photovoltaics (2015).
This paper studies non-Lambertian scattering and its impacts on the optical properties and device performance of the ultrathin GaAs single-junction solar cell with a reflective back scattering layer. Both a general GaAs cell design and the ultrathin cell design are carefully investigated. A Phong exponent m of ~12 is determined by fitting both simulated Jsc and EQE to their experimental values, with a more accurate averaged reflectivity of the textured Al0.52In0.48P/Au interface taken into account. Additionally, the measured open-circuit voltage (Voc) is lower than the best achievable value due to the nonradiative recombination in the device, and a limited lifetime of ~130 ns is determined by fitting the simulated and measured Voc; a specific series resistivity of 1.2 Ω•cm2 is determined to account for the 77.8% fill factor.